
Cofferdams are temporary enclosures to keep out water and soil so as to permit dewatering and construction of the permanent facility in the dry. A cofferdam is a temporary structure design to keep water and soil out of the excavation in which a bridge pier or other structure is built. Meaning of coffer Dam: Coffer = Box. To take up the foundation works in the marine region, it is necessary to obstruct the water flow by means of cofferdam.
PURPOSE TO USE COFFERDAM STRUCTURE
- To retain soil and water
- Main purpose is to provide dry working area for workers
- It is constructed to facilitate pile driving operation.
- It is used to place grillage as well as raft foundation
- It is used when the foundation for piers and abutments for a bridge, dams, locks etc are to be constructed.
- Some times it is also provided to store water temporarily
TYPES OF COFFER DAM
Considering the material used in their construction, cofferdam may be divided in to the following categories-
- Earthen Cofferdam
- Rockfill Cofferdam
- Single Walled Cofferdam
- Double Walled Cofferdam
- Braced Cofferdam
- Cellular Cofferdam
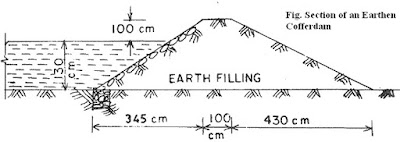
1. Earthen Cofferdam
Earthen cofferdam are constructed at place where the height of water is less say 3 meter and the current velocity is low. These dams are built using the local available material such as clay, fine sand or even soil. The height of the dam is kept 1m more than that of maximum water level. Free board of the dam or top of the dam is kept 1m so that the water does not enter the other side even when waves arises. The slope usually given but 1:1 or 1:2. The slope of the water side is pitched with rubble stones so that the water action does not score the embankment. Even sheet piles are driven in the center of the dam to resist water seepage. After the construction of earthen cofferdam the water from the other site is pumped out and construction is executed.
Earthen cofferdam are constructed at place where the height of water is less say 3 meter and the current velocity is low. These dams are built using the local available material such as clay, fine sand or even soil. The height of the dam is kept 1m more than that of maximum water level. Free board of the dam or top of the dam is kept 1m so that the water does not enter the other side even when waves arises. The slope usually given but 1:1 or 1:2. The slope of the water side is pitched with rubble stones so that the water action does not score the embankment. Even sheet piles are driven in the center of the dam to resist water seepage. After the construction of earthen cofferdam the water from the other site is pumped out and construction is executed.
2. Rockfill Cofferdam
Rockfill cofferdam are better than that of earthen cofferdam. These dams are preferred when the rock is easy available at the construction site. These dams are very pervious to prevent water from seeping an impervious membrane of soil is provided in the dam. The height of the dam is can be up to 3m. The slope can be maintained at 1:1.5 to 1:1.25. The slope on the water is pitched so as to protect dam from wave action.
 This type of cofferdam is preferred when the depth of water is more than 6m and area of construction is less. Usually this is used in construction of bridges. Wooden or timber sheets are driven in to the river bed on the perimeter of the area of construction. On the inside steel sheets are driven in to the river bed. This inside sheets are placed at equal distance with the help of wales which are bolted to both sheets for either side. To improve the stability of this type of cofferdam half filled bags of sand are placed on the both side of walls. The water from the inside is pumped out and the construction process is under taken.
This type of cofferdam is preferred when the depth of water is more than 6m and area of construction is less. Usually this is used in construction of bridges. Wooden or timber sheets are driven in to the river bed on the perimeter of the area of construction. On the inside steel sheets are driven in to the river bed. This inside sheets are placed at equal distance with the help of wales which are bolted to both sheets for either side. To improve the stability of this type of cofferdam half filled bags of sand are placed on the both side of walls. The water from the inside is pumped out and the construction process is under taken.
Double walled type of cofferdam are used when the area of construction site is large and depth of water is high. In this place use of single walled cofferdam becomes uneconomical as the supports are to be increased. So double walled cofferdam is used. The difference in one wall and double wall dam is that her it has two walls instead of walls for extra stability. This types of dams can hold water up to 12m high. Two piles are driven inside the water bed with a space in between and attached each other with wales with bolted connection. As the water depth increases the space between the walls increases. The space between the walls are filled with soil. To prevent the leakage from the ground below the sheet piles are driven to a good depth in the bed.
5. Braced Cofferdam
When it is difficult to drive piles inside the bed in the water then this type of cofferdam is used. In braced cofferdam two piles are driven in to the bed and they are laterally supported with the help of wooden crib installed in alternate course to form pockets. The empty pockets here are filled with stone and earth. The frame work of the cofferdam is prepared on the ground and then floated to the site where the cofferdam is to be constructed. The layers of sand and the other loose material overlaying the impervious hard bed is dredged out. Crib is then sunk to the position the bottom of each crib is given a shape to fit in the variation in the surface of bed rock. After the pit is dewatered the structure is constructed. When the concreting has been completed above the water level the cofferdam is removed.
6. Cellular Cofferdam
When the water layer is more than the 20m common types of cofferdam are uneconomical to use. In this situation cellular cofferdam are used. This type of dam is used in construction of dams, locks, weirs etc. Cellular cofferdam is made by driving straight web steel pile arranged to form a series of interconnected cells. The cells are constructed in various shapes and style to suit the requirement of site. Finally the cells are filled with clay, sand or gravels to make them stable against the various forces to which they are likely to be subjected to. The two common shapes of cellular cofferdam are-
- Circular Type Cellular Cofferdam
- Diaphragm Type Cellular Cofferdam
This type of cellular cofferdam consist of circular arcs on the inner and outer sides which are connected by straight diaphragm walls. The connection between the curved part and the diaphragm are made by means of a specially fabricated Y-element. The cofferdam is thus made from interconnected steel sheet piles. The empty space are filled with non pervious material like clay or sand. Due to the filling material the self weight of the membrane increases and leakage is reduced. One advantage of diaphragm type is that the effective length of the cofferdam may be increased easily by lenthening the diaphragm. Hence in case from design consideration it is necessary to have effective width of the cofferdam more than 21m diaphragm type cofferdam must be used.
(b). Diaphragm Type Cellular Cofferdam
It consist of a set of large diameter main circular cells interconnected by arcs of smaller cells. The walls of the connecting cells are perpendicular to the wall of the main circular cells of large diameter. The segmental arc are joined by special T-piles to the main cells. The circular type cellular cofferdam are self sustaining and therefore independent of the adjacent circular cells. Each cell can be filled independently. The Stability of such cells is much greater as compared with that of the diaphragm. type. However the circular cells are more expensive then the diaphragm type as these require more sheet piles and greater skill in setting and driving the piles. Because the diameter of circular cells is limited by interlock tension their ability to resist lateral pressure due to high head is limited.
CONSTRUCTION SEQUENCE OF COFFERDAM
For typical cofferdam such as for a bridge piers, the construction procedure generally is-
- Pre-dredge to remove soil or soft sediment and level the area of the cofferdam.
- Drive Temporary Support piles for template.
- Temporarily erect bracing frame on the support piles for the template.
- Install steel sheet piles starting at the all four corners and meeting at center of each side
- Drive sheet piles to grade.
- Block between bracing frame and sheets and provide ties for sheet piles at the top as necessary.
- Excavate inside the grade or slightly below grade while leaving the cofferdam full of water, Then lower the water inside and progressively install internal bracing as required by the design.
- Derive piles with in the cofferdam if required.
- Place rockfill as a leveling and support course.
- Place tremie concrete seal.







0 Comments: